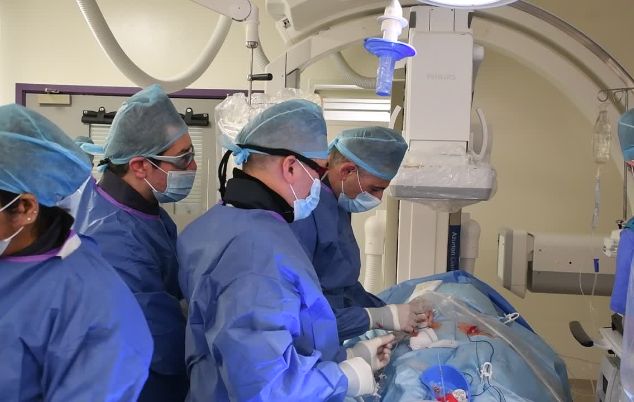
Royal Papworth Hospital is one of the leading and highest-volume centres in the UK for the management of heart rhythm problems.
The cardiac rhythm management team undertakes in excess of 1,500 diagnostic electrophysiology studies and ablation procedures per year, and an additional 1,500 cardiac implantable electronic device procedures.
When the heart beats abnormally fast, it is known as tachycardia and can be due to a number of different mechanisms. You might experience symptoms of palpitations, breathlessness, chest pain or dizziness.
The mechanism responsible for the tachycardia can often be identified by performing a diagnostic electrophysiology study. Areas of abnormal electrical activity can then be targeted by ablation to block electrical signals and prevent recurrence of abnormal heart rhythms. This often involves applying heat or cold to the areas concerned.
Diagnostic Electrophysiology Study (EPS)
During an EPS fine wires (catheters) are passed through a small tube inserted into a vein at the top of your leg. These are passed into the heart using x-rays to guide their placement. Once in position, the electrical activity of the heart can be mapped from the inside.
The heart can be stimulated using the wires to start the abnormal rhythm to help establish where the abnormal rhythm originates from.
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
This is a broad term which most commonly refers to the situation where an abnormal connection between the chambers of the heart can cause a repetitive electrical circuit to develop. Although this can be managed with tablets, it can often be successfully cured with.
SVT ablation
The abnormal connection can often be detected by performing an EPS. Once identified, ablation can destroy the abnormal connection and prevent recurrence of the SVT.
Atrial Flutter
Another common cause of tachycardia is atrial flutter. The occurs when the electrical circuit is continuous around the different structures in the top chambers of the heart.
Flutter ablation
A series of targeted ablation lesions can be delivered that blocks the electrical circuit and prevents it from being able to come back.
Atrial fibrillation (AF)
In atrial fibrillation the electrical signals in the top chambers of your heart have become scrambled. This causes the bottom chambers to beat in an erratic and often fast manner.
Cardioversion
Atrial fibrillation ablation
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) and cardiac arrest
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator
Ventricular tachycardia ablation
Consultants
Dr David Begley
Clinical Director for Cardiology
Specialist in Cardiac Rhythm Management
Dr Sharad Agarwal
Specialist in Cardiac Rhythm Management
Dr Simon Fynn
Specialist in Cardiac Rhythm Management
Dr Andrew Grace
Specialist in Cardiac Rhythm Management
Dr Patrick Heck
Clinical Lead for Cardiac Rhythm Management
Dr Claire Martin
Specialist in Cardiac Rhythm Management
Dr Greg Mellor
Specialist in Cardiac Rhythm Management
Dr Munmohan Virdee
Specialist in Cardiac Rhythm Management
Contacts
Arrhythmia specialist nurses
Tel: 01223 638947
Email: phn-tr.arrhythmia-nurses@nhs.net